Just want to make it clear, there are different ways to do the same thing, I’m just more comfortable working with this one because it fits to me. Well, before anything, let’s create our database. Since I’m not developing the whole application, all you have to do is pay attention to the field in your table that you want to be the “file storage”…
For those who prefer the design mode:
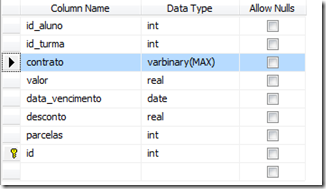
And for those who prefer sql mode:
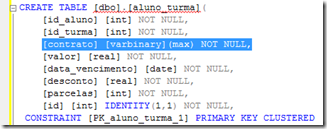
Alright, I will assume now that you already know how to work with linq, if you don’t my next article will probably talk about it. Anyway, I’m going to give you a heads up in three quick steps so you won’t feel lost.
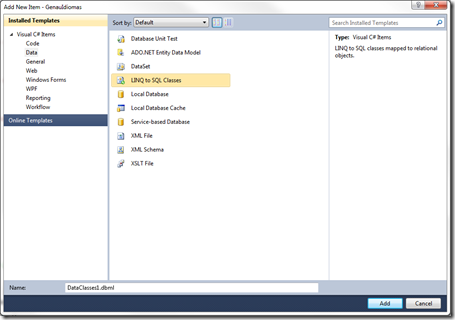
Add your .dbml file into your project.
Connect to your database using Server Explorer
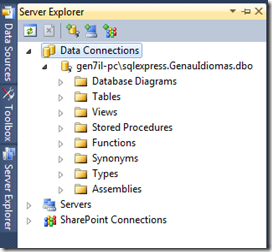
And then drag the table into your .dbml file.
Job done! For you to be able to use linq in your project, you cannot forget the using part.
using System.Data.Linq;
// using ProjectName.DBMLFolder;Alright, just one step more. Create your DataContext variable.
VariableDataContext dc = new VariableDataContext ();Ok, let’s go to the important part now! To get everything working, you’re going to need two methods.
1 – StreamFile is used to open a file and convert it in a byte array.
private byte[] StreamFile(string fileName)
{
// Open file
FileStream fs = new FileStream(fileName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
// ByteArray
byte[] ImageData = new byte[fs.Length];
// Read block of bytes
fs.Read(ImageData, 0, System.Convert.ToInt32(fs.Length));
// Close it
fs.Close();
// Return the byte data
return ImageData;
}2 – ByteArrayToFile is used to do the opposite way.
public bool ByteArrayToFile(string fileName, byte[] byteArray)
{
try
{
// Open file for reading
System.IO.FileStream fileStream = new System.IO.FileStream
(fileName, System.IO.FileMode.Create, System.IO.FileAccess.Write);
// Writes a block of bytes
fileStream.Write(byteArray, 0, byteArray.Length);
// Close file stream
fileStream.Close();
return true;
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
Console.WriteLine(exp.ToString());
}
return false;
}Alright, now all you have to do is call those methods properly.
1 – To insert a file in your database.
// Create your object
Class objClass = new Class();
// Create your table to insert
Table tbClass = dc.getTable();
// file to insert
byte[] fileByteArray = StreamFile("path");
// Converts it to Binary
// it can be done inside the method as well
Binary fileBinary = new Binary(fileByteArray);
// Fill object
objClass.file = fileBinary;
// Insert
tbClass.InsertOnSubmit(objClass);
// Submit it!2 – To get information from database and save the file. All you have to do is the opposite way.
// Create your table to insert
Table tbClass = dc.getTable();
// just get the first object inserted
// of course there must be an id equals to 1
Class objClass = tbClass.FirstOrDefault(p => p.id == 1);
if (ByteArrayToFile("new path", objClass.file))
{
// Well done!
}
else
{
// something wrong happened
}Pretty easy, huh? It helps me a lot since I’m currently working with SQL Server.
Well, if you like this quick tutorial, please help me sharing it! Doubts or comments are always welcome.
Thanks